Once again we see the Yen bouncing around 100….
There is still a lot of complacency worldwide. For example, car sales have been outstanding and our guess has been that a surge of better economic reports would be part of the final surge in the stock markets.
In early July, things started to deteriorate as regions from Turkey to Brazil to China and Indonesia were “getting hit by a brutal combination of events, as economies slow, investors pull out cash, commodity prices tumble and protesters take to the streets”. That’s how the Wall Street Journal wrote it up on July 2nd.
The news reminded of early July 1997 when the “Asian Crisis” roiled the Thai baht. It denied establishment boasts that the problem could be “isolated”. After traveling around Asia, eventually it fetched up in New York in that fateful September when the corporate bond market suffered its worst month in a decade.
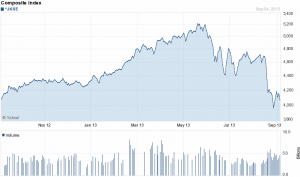
This time around, the “Asian” problem started in early-July and on August 29th Bloomberg reported “Stocks in Southeast Asia are tumbling at the fastest pace in 12 years relative to global equities”.
A chart of the Indonesian Stock Market
This has been accompanied by continued weakness in Emerging Market bonds (EMB), which makes sense. US Munis (MUB) also continue to decline and the Spanish Ten-Year yield is turning up. At the close it was up to 4.62%. Rising above 4.48% is a breakout. Lower-grade corporates (HYG and JNK) became oversold a couple of weeks ago and have rallied to resistance.
In Japan, the government has indebted itself to the tune of 230% of GDP… a total exceeding ONE QUADRILLION yen.
That’s a “1 with 15 zer000000000000000‘s after it. 1,000,000,000,000,000
And according to the Japanese government’s own figures, they spent a mind-boggling 24.3% of their entire national tax revenue just to pay interest on the debt last year!
Remember this adds a minimum 25 trillion more debt each year just on interest! Not to mention the other (again at minimum) 30 trillion in deficit spending to keep the wheels on Japan. The net minimum increase in annual debt is about 55 Trillion! At least!
Slowly, somewhere between this untenable fiscal position and the radiation leak at Fukushima, a few Japanese people realized that their confidence in the system was misguided.
We are helping an increasing number Japanese residents send some funds offshore.
Why? If the government defaults on its debts or ignites a currency crisis (both likely scenarios given the raw numbers), then those folks will at least preserve a portion of their savings intact. But if nothing happens and Japan limps along, they won’t be worse off for having some cash in a strong, stable, well-capitalized offshore banking jurisdiction. Where their funds are allocated and separated from bank assets, with no liens or encumbrances.
For Japan, the smart people who see the writing on the wall just want to be prepared with a sensible solution. They’re taking action before anything financially disastrous happens.
So what can you do?
- Open accounts in various jurisdictions and currencies.
- Invest in some physical assets outside your home country.
- Make sure gold / silver funds are fully backed by allocated bullion with no liens or encumbrances.
Don’t be complacent, be prepared.
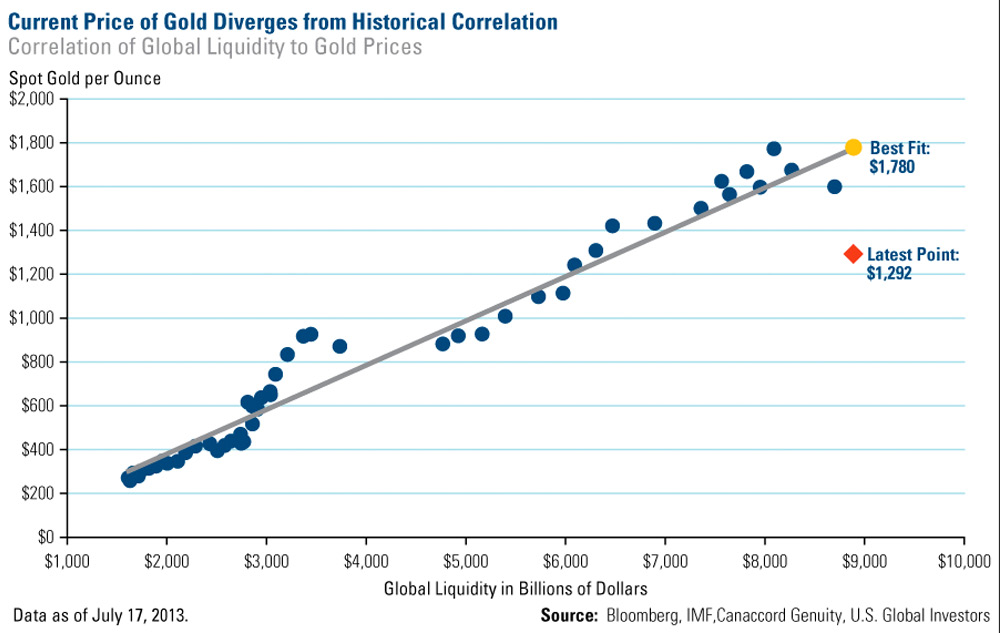
How far gold is off course?
Frank Holmes of US Global Investors is another who has forgotten more about the gold market
than many will ever know.
Here is his take on how far gold is off course:
Gold has been in extremely oversold territory lately despite drivers for the metal remaining in place.
Here’s a different way to look at how far gold has been off course. The chart below tracks the correlation of the price of an ounce of gold to global liquidity, with global liquidity defined as the sum of the U.S. monetary base and the foreign holdings of U.S. Treasuries. Since June 2000, as the U.S.’s monetary base and foreign holdings increased, so did the price of gold.
The correlation suggests the current level of liquidity supports a gold price of $1,780 per ounce, well above the current spot price around $1,300.
Source: US Global Investors
Do Western Central Banks Have Any Gold Left??? Part III
This was all orchestrated to increase supply and tame demand. We believe that central planners are now running out of options to suppress the gold price. After taking a pause, the secular gold bull market is set to continue.
http://sprottglobal.com/markets-at-a-glance/maag-article/?id=8044
The coming Japanese tax grab?
We have started to notice that more large wage earners in Japan are getting questions from the tax office . . . on overseas assets. So, have you set up your assets properly to legally avoid the coming Japanese tax grab?
In 2013 there is an effort to ensure that the taxable income arising from overseas assets is correctly and fully disclosed. Residents of Japan with assets held overseas worth over JPY50 million will be required to file a report disclosing those assets to the tax authorities. This new requirement is in addition to the “5 year rule” where all foreigners are taxable on their worldwide income after they have lived in Japan for 5 years.
Reporting requirement (50 million is about $500,000)
By 15 March of each year a Japan-resident taxpayer who holds overseas assets with a fair market value of more than JPY50 million as of 31 December of the previous year will be required to file a return declaring those assets. The first report will be due in March 2014 for assets held at 31 December 2013.
The location of assets is to be determined using the regulations applicable to inheritance tax. The table below shows the location for commonly held assets.
| Asset | Location |
| Immovable assets | Physical location of the asset |
| Cash deposits | Address of the branch where deposits are held |
| Bonds/Shares | Address of the head office of the issuer |
As a result the report will not only identify undeclared sources of foreign income, but could also be used in identifying overseas assets for inheritance tax purposes.
Penalties for non-compliance
The penalties for non-compliance are similar to those for the share based remuneration requirements above. If a taxpayer fails to file the report or deliberately files a false report, they a face a penalty of either a maximum of one year in prison or a maximum fine of JPY500,000. These penalties will apply to the second reporting period (for assets held at 31 December 2014) onwards. In addition the usual penalty for non-disclosure of income will be increased by 5% to 15% in cases where the underlying asset is not disclosed in this report. If the asset is disclosed, the penalty is reduced to 5% of the income.
Summary
The information disclosed in this report will aid the tax authority not only in identifying overseas sources of income, but also in ensuring that inheritance estates straddling multiple jurisdictions are fully disclosed. This is another sign of the increasingly aggressive stance the tax authority is taking to cross-border inheritances.
Banner Japan is able to assist with the setup of a variety of Japan tax compliant structures and solutions — call us today for a free consultation on what we can do to shield and grow your assets. Also it is always best to start planning early even if you assets are not quite yet at 50m. Those who plan will be better off.
These solutions and structures will also shield you from the “5 year rule” too – contact us now and we can have a discussion to minimize your Japan tax exposure.
European News
Reuters) – A draft law that a group of European Union lawmakers voted for on Monday would shield small depositors from losing their savings in future bank rescues, but customers with more than 100,000 euros in savings when a bank failed could suffer losses.
MORE: http://www.reuters.com/article/2013/05/20/us-eu-banks-idUSBRE94J0AC20130520
Japan government tax reform proposals for 2013
The new government released its 2013 tax reform proposals, please find a broad outline of the main items below.
Corporation tax
Companies that met the requirements could benefit from a JPY200,000 tax credit for each additional employee hired. This credit will increase to JPY400,000 per employee under the proposals.
Salary increase incentive
Employers that increase salaries by at least 5% would be able to benefit from a tax credit of 10% on the increase in the salary amount (capped at 10% of the corporation tax liability) under the new proposals. This would apply for financial years that begin between 1 April 2013 and 31 March 2016.
Entertainment expense deduction for SMEs
Currently SMEs are allowed to take a tax deduction for 90% of the first JPY6 million of entertainment expenses. The proposal would increase this to 100% of the first JPY8 million of expenses.
Individual income tax
The current highest rate of income tax is 40% on taxable income over JPY18 million. A new 45% rate will apply to taxable income over JPY40 million from 2015. Combined with the employment income deduction cap which applies from 2013 onwards this measure will increase the cost of tax equalization arrangements for executives seconded to Japan.
Inheritance and gift tax
The proposal included amendments to the scope, basic exemption and rate of inheritance tax and gift tax.
Scope: Under the current law when a foreign national with no domicile in Japan, inherits or receives a gift from a person with domicile in Japan, only the properties located in Japan are liable to Japanese inheritance or gift taxes. The proposal will widen this scope in this situation so that all properties, regardless of location, will be subject to tax in Japan. Although ostensibly this amendment is to reduce the scope for inheritance tax planning for Japanese high net worth individuals, it also affects expats, senior executives and entrepreneurs living in Japan.
Basic exemption
Currently an exemption of the first JPY50 million plus JPY10 million per statutory heir is available against inheritance estates. The proposals will reduce this to JPY30 million plus JPY6 million per heir.
Tax rate
Under the current rules, heirs pay inheritance at a top rate of 50% if their share of the estate after the basic exemption is greater than JPY300 million, and 40% is if their share is between JPY100 million and JPY300 million. The proposals will introduce a new top tax rate and additional bands as follows:
100 million to 200 million 40%
200 million to 300 million 45%
300 million to 600 million 50%
Over 600 million 55%
In addition, the top rate of gift tax will increase from 50% to 55%.
Consumption tax
In our August 2012 bulletin we discussed a new Consumption tax bill which will raise the rate of consumption tax in Japan from 5 % to 8% from 1 April 2014 to 30 September 2015, and to 10% from 1 October 2015 onwards.
At the time the Government was considering measures to prevent the rate rise from affecting those with low incomes disproportionately. The main measure included in the proposal related to housing loan credits. The purchase of residential housing incurs consumption tax in Japan and so the rate increase has a large effect on the size of mortgage needed to purchase a house. Currently a taxpayer can take an income tax credit equal to 1% of the outstanding loan capped at a loan amount of JPY 20 million for normal houses and JPY 30 million for certified environmentally-friendly houses. The credit period was due to expire at the end of 2013. The proposal extended this period to the end of 2017. In addition the maximum loan amount will be JPY 40 million and JPY 50 million respectively from 1 April 2014 if the rate increase remains in place.
Do Western Central Banks Have Any Gold Left???
From Eric Sprott and David Baker of Sprott Asset Management
Do Western Central Banks Have Any Gold Left???
Somewhere deep in the bowels of the world’s Western central banks lie vaults holding gargantuan piles of physical gold bars… or at least that’s what they all claim. The gold bars are part of their respective foreign currency reserves, which include all the usual fiat currencies like the dollar, the pound, the yen and the euro.
Collectively, the governments/central banks of the United States, United Kingdom, Japan, Switzerland, Eurozone and the International Monetary Fund (IMF) are believed to hold an impressive 23,349 tonnes of gold in their respective reserves, representing more than $1.3 trillion at today’s gold price. Beyond the suggested tonnage, however, very little is actually known about the gold that makes up this massive stockpile. Western central banks disclose next to nothing about where it’s stored, in what form, or how much of the gold reserves are utilized for other purposes. We are assured that it’s all there, of course, but little effort has ever been made by the central banks to provide any details beyond the arbitrary references in their various financial reserve reports.
Twelve years ago, few would have cared what central banks did with their gold. Gold had suffered a twenty year bear cycle and didn’t engender much excitement at $255 per ounce. It made perfect sense for Western governments to lend out (or in the case of Canada – outright sell) their gold reserves in order to generate some interest income from their holdings. And that’s exactly what many central banks did from the late 1980’s through to the late 2000’s. The times have changed however, and today it absolutely does matter what they’re doing with their reserves, and where the reserves are actually held. Why? Because the countries in question are now all grossly over-indebted and printing their respective currencies with reckless abandon. It would be reassuring to know that they still have some of the ‘barbarous relic’ kicking around, collecting dust, just in case their experiment with collusive monetary accommodation doesn’t work out as planned.
You may be interested to know that central bank gold sales were actually the crux of the original investment thesis that first got us interested in the gold space back in 2000. We were introduced to it through the work of Frank Veneroso, who published an outstanding report on the gold market in 1998 aptly titled, “The 1998 Gold Book Annual”. In it, Mr. Veneroso inferred that central bank gold sales had artificially suppressed the full extent of gold demand to the tune of approximately 1,600 tonnes per year (in an approximately 4,000 tonne market of annual supply). Of the 35,000 tonnes that the central banks were officially stated to own at the time, Mr. Veneroso estimated that they were already down to 18,000 tonnes of actual physical. Once the central banks ran out of gold to sell, he surmised, the gold market would be poised for a powerful bull market… and he turned out to be completely right – although central banks did continue to be net sellers of gold for many years to come.
As the gold bull market developed throughout the 2000’s, central banks didn’t become net buyers of physical gold until 2009, which coincided with gold’s final break-out above US$1,000 per ounce. The entirety of this buying was performed by central banks in the non-Western world, however, by countries like Russia, Turkey, Kazakhstan, Ukraine and the Philippines… and they have continued buying gold ever since. According to Thomson Reuters GFMS, a precious metals research agency, non-Western central banks purchased 457 tonnes of gold in 2011, and are expected to purchase another 493 tonnes of gold this year as they expand their reserves.1 Our estimates suggest they will likely purchase even more than that.2 The Western central banks, meanwhile, have essentially remained silent on the topic of gold, and have not publicly disclosed any sales or purchases of gold at all over the past three years. Although there is a “Central Bank Gold Agreement” currently in place that covers the gold sales of the Eurosystem central banks, Sweden and Switzerland, there has been no mention of gold sales by the very entities that are purported to own the largest stockpiles of the precious metal.3 The silence is telling.
Over the past several years, we’ve collected data on physical demand for gold as it has developed over time. The consistent annual growth in demand for physical gold bullion has increasingly puzzled us with regard to supply. Global annual gold mine supply ex Russia and China (who do not export domestic production) is actually lower than it was in year 2000, and ever since the IMF announced the completion of its sale of 403 tonnes of gold in December 2010, there hasn’t been any large, publicly-disclosed seller of physical gold in the market for almost two years.4 Given the significant increase in physical demand that we’ve seen over the past decade, particularly from buyers in Asia, it suffices to say that we cannot identify where all the gold is coming from to supply it… but it has to be coming from somewhere.
To give you a sense of how much the demand for physical gold has increased over the past decade, we’ve listed a select number of physical gold buyers and calculated their net change in annual demand in tonnes from 2000 to 2012 (see Chart A).
CHART A 
Numbers quoted in metric tonnes. † Source: CBGA1, CBGA2, CBGA3, International Monetary Fund Statistics, Sprott Estimates. †† Source: Royal Canadian Mint and United States Mint. ††† Includes closed-end funds such as Sprott Physical Gold Trust and Central Fund of Canada. ^ Source: World Gold Council, Sprott Estimates. ^^ Source: World Gold Council, Sprott Estimates. ^^^ Refers to annualized increase over the past eight years.
As can be seen, the mere combination of only five separate sources of demand results in a 2,268 tonne net change in physical demand for gold over the past twelve years – meaning that there is roughly 2,268 tonnes of new annual demand today that didn’t exist 12 years ago. According to the CPM Group, one of the main purveyors of gold statistics, the total annual gold supply is estimated to be roughly 3,700 tonnes of gold this year. Of that, the World Gold Council estimates that only 2,687 tonnes are expected to come from actual mine production, while the rest is attributed to recycled scrap gold, mainly from old jewelry.5 (See footnote 5). The reporting agencies have a tendency to insist that total physical demand perfectly matches physical supply every year, and use the “Net Private Investment” as a plug to shore up the difference between the demand they attribute to industry, jewelry and ‘official transactions’ by central banks versus their annual supply estimate (which is relatively verifiable). Their “Net Private Investment” figures are implied, however, and do not measure the actual investment demand purchases that take place every year. If more accurate data was ever incorporated into their market summary for demand, it would reveal a huge discrepancy, with the demand side vastly exceeding their estimation of annual supply. In fact, we know it would exceed it based purely on China’s Hong Kong gold imports, which are now up to 458 tonnes year-to-date as of July, representing a 367% increase over its purchases during the same period last year. If the imports continue at their current rate, China will reach 785 tonnes of gold imports by year-end. That’s 785 tonnes in a market that’s only expected to produce roughly 2,700 tonnes of mine supply, and that’s just one buyer.
Then there are all the private buyers whose purchases go unreported and unacknowledged, like that of Greenlight Capital, the hedge fund managed by David Einhorn, that is reported to have purchased $500 million worth of physical gold starting in 2009. Or the $1 billion of physical gold purchased by the University of Texas Investment Management Co. in April 2011… or the myriad of other private investors (like Saudi Sheiks, Russian billionaires, this writer, probably many of our readers, etc.) who have purchased physical gold for their accounts over the past decade. None of these private purchases are ever considered in the research agencies’ summaries for investment demand, and yet these are real purchases of physical gold, not ETF’s or gold ‘certificates’. They require real, physical gold bars to be delivered to the buyer. So once we acknowledge how big the discrepancy is between the actual true level of physical gold demand versus the annual “supply”, the obvious questions present themselves: who are the sellers delivering the gold to match the enormous increase in physical demand? What entities are releasing physical gold onto the market without reporting it? Where is all the gold coming from?
There is only one possible candidate: the Western central banks. It may very well be that a large portion of physical gold currently flowing to new buyers is actually coming from the Western central banks themselves. They are the only holders of physical gold who are capable of supplying gold in a quantity and manner that cannot be readily tracked. They are also the very entities whose actions have driven investors back into gold in the first place. Gold is, after all, a hedge against their collective irresponsibility – and they have showcased their capacity in that regard quite enthusiastically over the past decade, especially since 2008.
If the Western central banks are indeed leasing out their physical reserves, they would not actually have to disclose the specific amounts of gold that leave their respective vaults. According to a document on the European Central Bank’s (ECB) website regarding the statistical treatment of the Eurosystem’s International Reserves, current reporting guidelines do not require central banks to differentiate between gold owned outright versus gold lent out or swapped with another party. The document states that, “reversible transactions in gold do not have any effect on the level of monetary gold regardless of the type of transaction (i.e. gold swaps, repos, deposits or loans), in line with the recommendations contained in the IMF guidelines.”6 (Emphasis theirs). Under current reporting guidelines, therefore, central banks are permitted to continue carrying the entry of physical gold on their balance sheet even if they’ve swapped it or lent it out entirely. You can see this in the way Western central banks refer to their gold reserves. The UK Government, for example, refers to its gold allocation as, “Gold (incl. gold swapped or on loan)”. That’s the verbatim phrase they use in their official statement. Same goes for the US Treasury and the ECB, which report their gold holdings as “Gold (including gold deposits and, if appropriate, gold swapped)” and “Gold (including gold deposits and gold swapped)”, respectively (see Chart B). Unfortunately, that’s as far as their description goes, as each institution does not break down what percentage of their stated gold reserves are held in physical, versus what percentage has been loaned out or swapped for something else. The fact that they do not differentiate between the two is astounding, (Ed. As is the “including gold deposits” verbiage that they use – what else is “gold” supposed to refer to?) but at the same time not at all surprising. It would not lend much credence to central bank credibility if they admitted they were leasing their gold reserves to ‘bullion bank’ intermediaries who were then turning around and selling their gold to China, for example. But the numbers strongly suggest that that is exactly what has happened. The central banks’ gold is likely gone, and the bullion banks that sold it have no realistic chance of getting it back.
CHART B 
Sources: 1) http://www.bankofengland.co.uk/statistics/Documents/reserves/2012/Aug/tempoutput.pdf 2) http://www.treasury.gov/resource-center/data-chart-center/IR-Position/Pages/08312012.aspx 3) http://www.ecb.int/stats/external/reserves/html/assets_8.812.E.en.html 4) http://www.boj.or.jp/en/about/account/zai1205a.pdf 5) http://www.imf.org/external/np/exr/facts/gold.htm 6) http://www.snb.ch/en/mmr/reference/annrep_2011_komplett/source
Notes: ECB Data as of July 2012. Bank of Japan data as of March 31, 2012.
* European Central Bank reserves is composed of reserves held by the ECB, Belgium, Germany, Estonia, Ireland, Greece, Spain, France, Italy, Cyprus, Luxembourg, Malta, The Netherlands, Austria, Portugal, Slovenia, Slovakia and Finland. ** Bank of Japan only lists its gold reserves in Yen at book value.
Our analysis of the physical gold market shows that central banks have most likely been a massive unreported supplier of physical gold, and strongly implies that their gold reserves are negligible today. If Frank Veneroso’s conclusions were even close to accurate back in 1998 (and we believe they were), when coupled with the 2,300 tonne net change in annual demand we can easily identify above, it can only lead to the conclusion that a large portion of the Western central banks’ stated 23,000 tonnes of gold reserves are merely a paper entry on their balance sheets – completely un-backed by anything tangible other than an IOU from whatever counterparty leased it from them in years past. At this stage of the game, we don’t believe these central banks will be able to get their gold back without extreme difficulty, especially if it turns out the gold has left their countries entirely. We can also only wonder how much gold within the central bank system has been ‘rehypothecated’ in the process, since the central banks in question seem so reluctant to divulge any meaningful details on their reserves in a way that would shed light on the various “swaps” and “loans” they imply to be participating in. We might also suggest that if a proper audit of Western central bank gold reserves was ever launched, as per Ron Paul’s recent proposal to audit the US Federal Reserve, the proverbial cat would be let out of the bag – with explosive implications for the gold price.
Notwithstanding the recent conversions of PIMCO’s Bill Gross, Bridegwater’s Ray Dalio and Ned Davis Research to gold, we realize that many mainstream institutional investors still continue to struggle with the topic. We also realize that some readers may scoff at any analysis of the gold market that hints at “conspiracy”. We’re not talking about conspiracy here however, we’re talking about stupidity. After all, Western central banks are probably under the impression that the gold they’ve swapped and/or lent out is still legally theirs, which technically it may be. But if what we are proposing turns out to be true, and those reserves are not physically theirs; not physically in their possession… then all bets are off regarding the future of our monetary system. As a general rule of common sense, when one embarks on an unlimited quantitative easing program targeted at the employment rate (see QE3), one had better make sure to have something in the vault as backup in case the ‘unlimited’ part actually ends up really meaning unlimited. We hope that it does not, for the sake of our monetary system, but given our analysis of the physical gold market, we’ll stick with our gold bars and take comfort as they collect more dust in our vaults, untouched.
| 1 | http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2012-09-04/central-bank-gold-buying-seen-reaching-493-tons-in-2012-by-gfms.html |
| 2 | See notes in Chart A. |
| 3 | http://www.gold.org/government_affairs/reserve_asset_management/central_bank_gold_agreements/ |
| 4 | http://www.imf.org/external/np/exr/faq/goldfaqs.htm |
| 5 | Mine supply estimate supplied by World Gold Council; YTD gold mine production data suggests that total 2012 gold mine supply will come in lower around 2,300 tonnes, ex Russia and China production. In addition, Frank Veneroso has recently published a new report that warns that the supply of recycled scrap gold could drop significantly going forward due to the depletion ofthe inventories of industrial scrap and long held jewelry over the past decade. |
| 6 | http://www.ecb.int/pub/pdf/other/statintreservesen.pdf |
Part 2
Do Western Central Banks Have Any Gold Left? Part II (part 1 here)
The past few months have been difficult for the gold investor as selling pressure in the gold futures market has set a decidedly negative direction for the price of the yellow metal. As fundamental investors, we always pay special attention to the supply and demand dynamics of gold and, recently, we have found it very difficult to reconcile lower prices with continued strong demand for physical gold.
While the supply of gold has remained largely static, we have seen a steady increase in demand for the yellow metal. India and China have emerged as strong buyers, consuming over half of the mine supply in recent years. Central banks have switched from being sellers of gold to being net buyers, with their gold purchases in 2012 increasing by 17% to almost 535 tonnes. Exchange traded products (ETPs) around the world have continued to add to their gold hoards, as have institutions and private investors. Furthermore, central banks, such as South Korea and Russia, have added to their bullion reserves early in 2013, which points to sustained strength in demand. These facts are important because, over the past decade, the annual supply of gold has stayed flat at approximately 4,000 tonnes.
Much ado has been made about the recent sell-off in the yellow metal forcing certain ETPs to liquidate, adding a supply of gold into the market in the process. Our work reveals that the previous ETP sell-offs, (which occurred in January 2011, December 2011, May 2012 and July 2012) have all coincided with gold finding strong price support and rallying higher.
In our September 2012 MAAG, titled, “Do Western Central Banks Have Any Gold Left???”, we reconciled the annual change in demand for gold between 2000 and 2012 to be almost 2,300 tonnes. We went on to hypothesize that given the massive change in demand, the only suppliers large enough to fill the gap between supply and demand were the Central Banks. Now, our long search for the “smoking gun” to prove our hypothesis appears to have finally materialized.
Every month, the US Census Bureau releases the FT900 document, which outlines US International Trade Data. Going through this document, we were intrigued to see that in December 2012 the US exported over $4B worth of gold and imported around $1.5B worth of gold, representing a net export of $2.5B or almost 50 tonnes1. This surprising number led us to look at the previous releases of US International Trade Data which go as far back as 1991 – what we found was truly shocking. Not only has the US been consistently exporting large quantities of gold on a net basis, the amount of gold the US has been exporting is above and beyond what the US should be capable of exporting.
The gold market is fairly simple to understand from a supply and demand perspective. Since you cannot fabricate gold out of thin air, supply comes from new mine production, scrap gold recycling and investor disposition of bullion. Demand comes from many sources including investment demand, electronics, dental and industrial uses to name a few. There can be short-term aberrations between supply and demand where the market can be oversupplied, or demand can outstrip supply, however, over a longer period, supply should equal demand with the price acting as the equalizer. Under this assumption, the amount of gold that the US is exporting should equate to the amount of gold that the US is not consuming over a long enough time frame.
Table 1 lays out our framework for analyzing the US gold supply and demand.
Table 1 
For our analysis of supply and demand, we have very robust statistics as far as mine production, import-export data, coin sales and ETP demand from GFMS2, the US Census Bureau3, the US Mint4 and Bloomberg5, respectively. We have good data on gold recycling, jewelry sales and gold use in electronics and industrial applications from the CPM Group6.
Table 2 lays out our analysis for 2012 using the supply and demand framework.
Table 2 
We used this framework to analyze supply and demand in the US going all the way back to 1991, which is as far back as the FT900 documents go. Over the span of 22 years, the total amount of gold that the US has exported – above and beyond its supply capability – is almost 4,500 tonnes! A truly stunning figure. (See Table 3).
TABLE 3: US GOLD MARKET, CUMULATIVE SUPPLY DEMAND 1991-2012 (IN TONNES) 

Admittedly there is an unknown in our analysis, that being gold bullion acquisition and disposition by private investors. However, strong demand in ETPs such as GLD and PHYS and demand for gold coins provide strong evidence that the private investor has been a net buyer over the years. The inclusion of the private investor on the demand side would in fact skew the ‘gap’ of 4,500 tonnes higher to a figure that would lie somewhere between 4,500 tonnes and 11,200 tonnes, which represents the gross exports out of the US. The only US seller that would be capable of supplying such an astonishing amount of gold is the US Government, with a reported gold holding of 8,300 tonnes. The US Government gold holdings have not been audited or verified in more than four decades. The US trade data defines the export of nonmonetary gold as a sale of gold from a private seller within the US to an official agency. In September 2012, we espoused that the Western Central Banks have been surreptitiously selling/ leasing their gold through private channels in an effort to increase the available supply and in turn suppress prices. This new analysis using official US agency numbers seems to provide the strongest validation of our hypothesis to date. It is worth noting that our data only covers two decades and that the export ‘gap’ could in fact be significantly larger if earlier numbers were included or the real private investor demand for gold was known.
We are currently in an environment where policy makers are intent on devaluing their currencies in an effort to create growth. Real rates continue to stay negative in most of the developed world. Every marginal dollar of debt that is created is producing lower and lower amounts of growth. In a world overwhelmed by mountains of debt and economic growth which is sub-par at best, precious metals and real assets can act as insurance against the stupidity of policy makers. The evidence pointing towards the suppression of the gold price is becoming increasingly apparent. Don’t be the last person to figure this out! The current sell-off in gold should be viewed not with extreme trepidation but as an unbelievable opportunity to buy the metal at an artificially low value.
| 1 | Import Export Stats – US Census Foreign trade: http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/index.html |
| 2 | GFMS – http://www.gfms.co.uk/ |
| 3 | Import Export Stats – US Census Foreign trade: http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/index.html |
| 4 | Coin sales from US Mint: http://www.usmint.gov/ |
| 5 | Bloomberg |
| 6 | Jewelry, recycling, dental, electronics and industrial from CPM Gold Yearbook |
Japan the yen and Gold
http://media.chicagobooth.edu/mediasite/Viewer/?peid=f15d95d054e8442ab0cc1c60321383101d
Kyle Bass, addressing Chicago Booth’s Initiative on Global Markets last week, clarified his thesis on Japan in great detail, but it was the Q&A that has roused great concern. “The AIG of the world is back – I have 27 year old kids selling me one-year jump risk on Japan for less than 1bp – $5bn at a time… and it is happening in size.” As he explains, the regulatory capital hit for the bank is zero (hence as great a return on capital as one can imagine) and “if the bell tolls at the end of the year, the 27-year-old kid gets a bonus… and if he blows the bank to smithereens, ugh, he got a paycheck all year.” Critically, the bank that he bought the ‘cheap options’ from recently called to ask if he would close the position – “that happened to me before,” he warns, “in 2007 right before mortgages cracked.” His single best investment idea for the next ten years is, “Sell JPY, Buy Gold, and go to sleep,” as he warns of the current situation in markets, “we are right back there! The brevity of financial memory is about two years.”
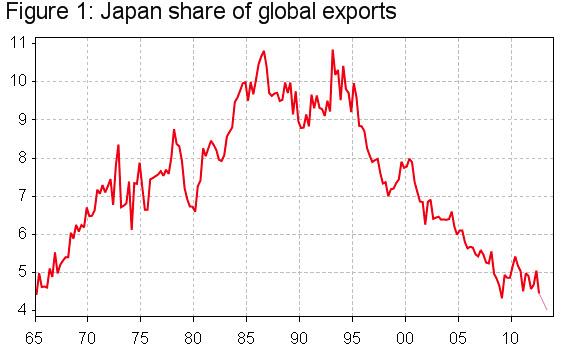
Japan’s share of the worlds exports . . .
The degree to which yen depreciation affects global trade is not what it used to be when Japan had a 10+% share. Its export share is now about 40% of what it was in the mid-1990s and falling.
There is a strong academic case that countries with deflation and zero rates should be allowed to pursue a weaker currency openly as a policy tool. The reason is that there is no real conventional monetary tool they have left and if they are in a true liquidity/deflation trap, adding more domestic liquidity will not have much impact on real rates. The only way to get activity going may be to crowd in both exports and inflation via a weaker currency.